Appearance
Text
- Draws text with default or custom styling.
Textalways takes as little space as possible.- If the text string is long, the element may take the entire width and break to the next line.
- This element supports paging.
For most cases, that do not require any complex formatting, the simplified version of the Text component is enough as illustrated below.
c#
.Text("Sample text")
.Text("Red big text").FontColor("#F00").FontSize(24)Use the "text block" approach when you want to change style in the middle of a text string, inject page numbers or include custom components, as shown below:
c#
.Text(text =>
{
text.Span("This is a normal text, followed by some ");
text.Span("underlined text.").Underline();
});
Basic font style
You can define the text style using the following fluent API methods:
c#
.FontColor("#F00")
.FontFamily("Times New Roman")
// you can also provide fallback font families
.FontFamily("Times New Roman", "Calibri" "Noto Color Emoji")
.FontSize(24)
.LineHeight(1.5f)
.Italic()
.BackgroundColor(Colors.Grey.Lighten5)
.Strikethrough()
.Underline()
.Subscript()
.Superscript()Default text style within a block
Use these fluent API methods to adjust text position:
c#
.Text(text =>
{
text.DefaultTextStyle(x => x.FontSize(20).BackgroundColor(Colors.Green.Lighten3));
text.Line("Text following default style.");
text.Line("Text with altered style.").Underline();
});Font weight
You can easily set up font weight by using one of the following fluent API methods:
c#
.Weight(FontWeight.Normal)
.Thin()
.ExtraLight()
.Light()
.NormalWeight()
.Medium()
.SemiBold()
.Bold()
.ExtraBold()
.Black()
.ExtraBlack()Please notice that not all fonts support every weight. QuestPDF will match the closest available weight:

Subscript and superscript
c#
.Text(text =>
{
text.DefaultTextStyle(x => x.FontSize(20));
text.ParagraphSpacing(10);
var highlight = TextStyle.Default.BackgroundColor(Colors.Green.Lighten3);
text.Span("E=mc").Style(highlight);
text.Span("2").Superscript().Style(highlight);
text.Span(" is the equation of mass–energy equivalence.");
text.EmptyLine();
text.Span("H").Style(highlight);
text.Span("2").Subscript().Style(highlight);
text.Span("O").Style(highlight);
text.Span(" is the chemical formula for water.");
});
Line height
This settings changes spacing between text lines. Modify the value to make the text more compact or easier to read.
c#
.Column(column =>
{
var lineHeights = new[] { 0.8f, 1f, 1.5f };
var paragraph = Placeholders.Paragraph();
foreach (var lineHeight in lineHeights)
{
column
.Item()
.Border(1)
.Padding(10)
.Text(paragraph)
.FontSize(16)
.LineHeight(lineHeight);
}
});
Letter spacing
Letter spacing allows you to increase or decrease space between characters. This setting is useful when you want to make the text more compact (by decreasing letter spacing) or easier to read (by increasing letter spacing):
- The value 0 corresponds to the normal spacing defined by a font.
- Positive values create additional space.
- Negative values reduce space between characters.
This settings uses relative units. Example: let's assume your text has font size 20. If letter spacing is set to 0.1, an additional space of 2 points will be added between characters.
c#
.Column(column =>
{
var letterSpacing = new[] { -0.05f, 0f, 0.2f };
var paragraph = Placeholders.Sentence();
foreach (var spacing in letterSpacing)
{
column
.Item()
.Border(1)
.Padding(10)
.Column(nestedColumn =>
{
nestedColumn
.Item()
.Text(paragraph)
.FontSize(18)
.LetterSpacing(spacing);
nestedColumn
.Item()
.Text($"Letter spacing of {spacing} em")
.FontSize(14)
.Italic()
.FontColor(Colors.Blue.Medium);
});
}
});
Word Spacing
Word spacing allows you to increase or decrease space between words. This setting is useful when you want to make the text more compact (by decreasing word spacing) or easier to read (by increasing word spacing):
- The value 0 corresponds to the normal spacing defined by a font.
- Positive values create additional space.
- Negative values reduce space between characters.
This settings uses relative units. Example: let's assume your text has font size 20. If letter spacing is set to 0.1, an additional space of 2 points will be added between characters.
c#
.Column(column =>
{
var wordSpacing = new[] { -0.2f, 0f, 0.2f };
var paragraph = Placeholders.Sentence();
foreach (var spacing in wordSpacing)
{
column
.Item()
.Border(1)
.Padding(10)
.Column(nestedColumn =>
{
nestedColumn.Item()
.Text(paragraph)
.FontSize(16)
.WordSpacing(spacing);
nestedColumn.Item()
.Text($"Word spacing of {spacing} em")
.FontSize(10)
.Italic()
.FontColor(Colors.Blue.Medium);
});
}
});
Typography pattern
Please consider an example Typography class that describes text styling across all documents:
c#
// single typography class can help with keeping a consistent look & feel in the document
public static class Typography
{
public static TextStyle Title => TextStyle
.Default
.FontType("Helvetica")
.FontColor(Colors.Black)
.FontSize(20)
.Bold();
public static TextStyle Headline => TextStyle
.Default
.FontType("Helvetica")
.FontColor(Colors.Blue.Medium)
.FontSize(14);
public static TextStyle Normal => TextStyle
.Default
.FontType("Helvetica")
.FontColor("#000000")
.FontSize(10)
.LineHeight(1.25f)
.AlignLeft();
}Then, a predefined typography can be used in the following way:
c#
.Text("My text with predefined style").Style(Typography.Headline);Text alignment
Use the following fluent API methods to adjust text position:
c#
.Text(text =>
{
// pick alignment
text.AlignLeft();
text.AlignCenter();
text.AlignRight();
text.AlignStart();
text.AlignEnd();
text.Justify();
text.Span("Sample text");
});You can also use the shorthand version:
c#
.Text("Sample text").Justify();Example:
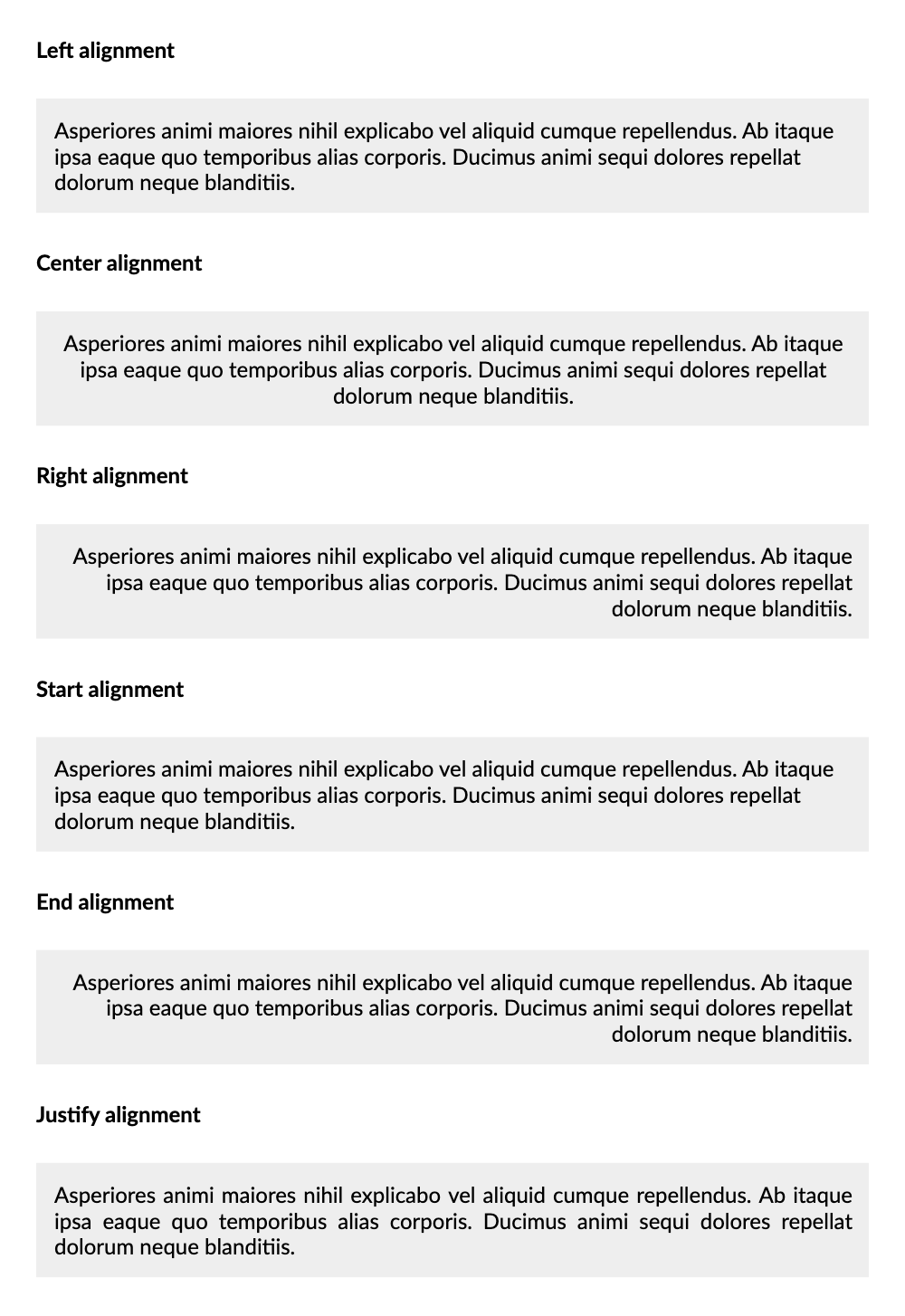
c#
var text = Placeholders.Paragraph();
content.Padding(20).Column(column =>
{
column.Spacing(20);
IContainer BlockStyle(IContainer container) => container.Background(Colors.Grey.Lighten3).Padding(10);
column.Item().Text("Left alignment").Bold();
column.Item().Element(BlockStyle).Text(text).AlignLeft();
column.Item().Text("Center alignment").Bold();
column.Item().Element(BlockStyle).Text(text).AlignCenter();
column.Item().Text("Right alignment").Bold();
column.Item().Element(BlockStyle).Text(text).AlignRight();
column.Item().Text("Start alignment").Bold();
column.Item().Element(BlockStyle).Text(text).AlignStart();
column.Item().Text("End alignment").Bold();
column.Item().Element(BlockStyle).Text(text).AlignEnd();
column.Item().Text("Justify alignment").Bold();
column.Item().Element(BlockStyle).Text(text).Justify();
});
Paragraph spacing
Paragraph spacing is the space added between paragraphs to improve readability and structure in a document. Its purpose is to visually separate paragraphs, making the text easier to navigate and more aesthetically pleasing.
c#
.Text(Placeholders.Paragraphs())
.ParagraphSpacing(10);
First line indentation
Paragraph first line indentation is the practice of indenting the first line of a paragraph by a specified amount. Its purpose is to visually distinguish the beginning of a new paragraph, enhancing the document's readability and structure.
c#
.Text(Placeholders.Paragraphs())
.ParagraphFirstLineIndentation(20);
Clamping lines with ellipsis
Line clamping is a technique used to limit the number of lines displayed for a block of text, truncating the content and often adding an ellipsis ("...") to indicate that there is more text not currently visible. Its purpose is to manage text overflow and maintain a clean layout in user interfaces.
c#
// when using shorthand Fluent API
.Text(Placeholders.Paragraph())
.ClampLines(3);
// or when using tech-rich Fluent API
.Text(text =>
{
text.ClampLines(3);
text.Span("Paragraph: ").Bold;
text.Span(Placeholders.Paragraph());
});
It is also possible to customize the ellipsis:
c#
.Text(Placeholders.Paragraph())
.ClampLines(3, " [...]");
Font Features
Font features are a set of typographic features that can be applied to text to enhance its appearance. They are used to control various aspects of text rendering.
To better understand what font features are, please consider example definitions. Please note that there are many more various font features. Most fonts support only a handful of them, having some of them enabled by default:
- Ligatures in typography are specific character combinations that are designed to improve the aesthetics and readability of certain letter pairs. For example, in some fonts, when you type certain combinations of letters like 'fi' or 'fl', they will be replaced with a single, joined glyph.
- Kerning in typography refers to the adjustment of space between characters in a proportional font. It's used to achieve a visually pleasing result by adjusting the spacing of specific character pairs. For example, in many fonts, the pair 'AV' is kerned so that the 'A' and 'V' are closer together than they would be by default.
Font features are always encoded as 4-character long strings. For example, the ligatures feature is encode as liga, while the kernig feature as kern. For a list of available features, refer to the QuestPDF.Helpers.FontFeatures class.
TIP
Please note that fonts usually support only a subset of font features. If you try to enable a feature that is not supported by the font, it will be ignored. Moreover, some fonts have features enabled by default, and you may not see any difference when enabling them.
c#
.Row(row =>
{
row.Spacing(25);
row.RelativeItem().Column(column =>
{
column.Item().Text("Without ligatures").FontSize(16);
column.Item().Text("fly and fight").FontSize(32).DisableFontFeature(FontFeatures.StandardLigatures);
});
row.RelativeItem().Column(column =>
{
column.Item().Text("With ligatures").FontSize(16);
column.Item().Text("fly and fight").FontSize(32).EnableFontFeature(FontFeatures.StandardLigatures);
});
});
Injecting custom content
Sometimes you may need to inject custom components between text spans. Every injected element is aligned to the baseline.
c#
.Text(text =>
{
text.Span("This is a random image aligned to the baseline: ");
text.Element().Height(24).Width(48).Image(Placeholders.Image);
text.Span(".");
});
Use negative padding to adjust element position to suit your needs:
c#
.Text(text =>
{
text.DefaultTextStyle(x => x.FontSize(20));
text.Span("This is a random image aligned to the baseline: ");
text.Element()
.PaddingBottom(-6)
.Height(24)
.Width(48)
.Image(Placeholders.Image);
text.Span(".");
});
DANGER
When injecting custom elements inside a text block, please remember to always constrain its size. Otherwise, the element will take entire available space.
Page numbers
Document
Use new text elements to inject pagination data, i.e. the current page number, the total page count in the document, etc.
c#
.Text(text =>
{
text.CurrentPageNumber();
text.TotalPages();
// it is also possible to style the text
text.CurrentPageNumber().Underline();
});Sections
It is possible to retrieve pagination data for a named section of your document.
c#
// define your section somewhere in the document:
.Section("customSection")
// refer to this location position in your list of contents:
.Text(text =>
{
// page number where section begins
text.BeginPageNumberOfSection("customSection");
// page number where section ends
text.EndPageNumberOfSection("customSection");
// page number relative to section beginning
// at section beginning page, method returns 1
text.PageNumberWithinSection("customSection");
// how many pages section takes
text.TotalPagesWithinSection("customSection");
});Formatting
It is possible to format the page number using the Format method.
c#
.Text(text =>
{
// assumes that FormatAsRomanNumeral
text.CurrentPageNumber().Format(FormatAsRomanNumeral);
static string FormatAsRomanNumeral(int? pageNumber)
{
if (pageNumber == null)
return "-------";
// proper implementation
return "MMXXII";
}
});Please note that the formatting function takes the int? type. QuestPDF uses a two-pass rendering algorithm whereby page numbers are only known during the second pass. In the first phase, your formatting method receives null to indicate that the page number is not yet determined. Please return any text that matches the expected output in length.
Section link
c#
// define your section somewhere in the document:
.Section("customLocationName")
// create a hyperlink to that location
.Text(text =>
{
text.SectionLink("Custom location link", "customLocationName");
});Hyperlink
c#
.Text(text =>
{
text.Hyperlink("Please visit QuestPDF website", "https://www.questpdf.com");
});Unicode support
The library supports text shaping capability, which is useful when generating advanced Unicode-capable text:
c#
.Padding(35)
.MinimalBox()
.Background(Colors.Grey.Lighten2)
.Text(text =>
{
text.DefaultTextStyle(TextStyle.Default.FontSize(20));
text.Span("Complex Unicode structure: ");
text.Span("T̶̖̔͆͆̽̔ḩ̷̼̫̐̈́̀͜͝͝ì̶͇̤͓̱̣͇͓͉̎s̵̡̟̹͍̜͉̗̾͛̈̐́͋͂͝͠ͅ ̴̨͙͍͇̭̒͗̀́͝ì̷̡̺͉̼̏̏̉̌͝s̷͍͙̗̰̖͙̈̑̂̔͑͊̌̓̊̇͜ ̶̛̼͚͊̅͘ṭ̷̨̘̣̙̖͉͌̏̂̅͑̄̽̕͝ȅ̶̲̲̙̭͈̬̣͔̝͔̈́͝s̸̢̯̪̫͓̭̮̓̀͆͜ț̸̢͉̞̥̤̏̌̓͝")
.FontFamily(Fonts.Calibri)
.FontColor(Colors.Red.Medium);
text.Span(".");
});
Advanced languages support
Text shaping capability also gives basic support for more advanced languages that:
- Display multiple text characters as a single glyph.
- Are displayed using right-to-left script.
c#
var text = "في المعلوماتية أو الرياضيات، خوارزمية الترتيب هي خوارزمية تمكن من تنظيم مجموعة عناصر حسب ترتيب محدد.";
.Padding(20)
.ContentFromRightToLeft()
.Text(text)
.FontFamily(Fonts.Calibri)
.FontSize(22);
Font fallback
Each font file contains a well-specified set of glyphs. Sometimes, to reduce font file size, more advanced glyphs are not present. For example, English uses around one hundred characters, whereas Chinese requires thousands of glyphs. Therefore, it is possible that text in a document may contain glyphs not available in the configured font. In such cases, an ugly character (usually a square with a question mark) is rendered.
You can define font fallback in the TexStyle object:
c#
TextStyle
.Default
.FontFamily(Fonts.Calibri, "Segoe UI Emoji");Dealing with pageable text
The Text element supports paging. That means part of the text may be moved to the next page if there is not enough space on the current one. There are several approaches to simplify the workflow with text as described below.
To make sure that text is never paged and always fully visible on a single page, please use the ShowEntire element:
c#
.ShowEntire()
.Text("A long text here will not be paged.");Sometimes, there is very little space on the page. It is enough to display a couple of lines but such a short text block may look awkward. In such cases, it is better to move the text block to the next page instead of attempting to perform line breaking. Please adjust the minimum height in the EnsureSpace element to match the desired minimum space to display at the end of the page.
c#
.EnsureSpace(50)
.Text("A long text here.");Forcing text direction (RTL)
QuestPDF automatically detects text direction and applies proper text alignment. However, it is possible to override text direction.
c#
TextStyle.Default.DirectionAuto() // default
TextStyle.Default.DirectionFromLeftToRight()
TextStyle.Default.DirectionFromRightToLeft()This may be useful with more advanced edge cases:
c#
.DefaultTextStyle(x => x.FontSize(24).FontFamily("Calibri"))
.Column(column =>
{
column.Spacing(10);
var word = "الجوريتم";
var definition = "algorithm in Arabic";
var text = $"{word} - {definition}";
// text direction is automatically detected using the first word
column.Item().Text(text);
// it is possible to force specific content direction
column.Item().Text(text).DirectionFromLeftToRight();
column.Item().Text(text).DirectionFromRightToLeft();
// to combine text in various content directions, split it into segments
column.Item().Text(text =>
{
text.Span(word);
text.Span(" - ");
text.Span(definition);
});
});